Power plants need transformers to work properly. Without them, the electricity generated would be lost during transmission, costing billions and leaving communities without power.
Power plants use step-up transformers to increase voltage for efficient transmission and generator transformers to connect generators to the grid. Different power plants may use specialized transformers like GSU transformers for thermal plants or three-phase transformers for hydroelectric facilities.
 at an electrical substation Power plant transformers in operation](https://voltoritransformer.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/image-1-power-plant-transformers-a-detailed-3d.png)
Transformers are the unsung heroes of our electrical grid. They work silently behind the scenes, ensuring electricity reaches our homes and businesses efficiently. I've visited dozens of power plants across Canada, and I'm always impressed by these engineering marvels that make modern life possible.
Which Transformer Is Used In A Power Plant?
Power plants face a critical problem: generated electricity must travel long distances without massive energy losses. Without proper transformers, power companies would lose millions in wasted energy.
Power plants primarily use generator step-up (GSU) transformers that increase voltage from 15-25kV to transmission levels of 138-765kV. They also employ station service transformers for internal operations and auxiliary transformers for backup systems and specific equipment needs.
Power plants rely on several types of transformers working together to ensure efficient electricity generation and distribution. Let me break this down based on my experience designing custom transformers for Canadian power facilities.
Primary Transformer Types in Power Plants
| Transformer Type | Function | Typical Capacity Range |
|---|---|---|
| Generator Step-Up (GSU) | Increases generator voltage for transmission | 100-1500 MVA |
| Station Service | Powers plant equipment and systems | 5-50 MVA |
| Auxiliary | Supplies specific systems or backup power | 1-25 MVA |
| Excitation | Controls generator field current | 0.5-5 MVA |
When I visited a thermal plant in Alberta last year, I saw firsthand how these transformers work together. The GSU transformers were massive units housed in their own containment areas with sophisticated cooling systems. These transformers must handle enormous loads continuously while maintaining 99.9% reliability. The design must account for thermal expansion, magnetic flux containment, and emergency cooling capabilities, as failure could lead to plant shutdown costing hundreds of thousands per day.
What Is The Main Transformer In A Power Plant?
When a power plant's main transformer fails, the entire facility can shut down, causing blackouts across communities and millions in economic damage. This critical component cannot be overlooked.
The main transformer in a power plant is the Generator Step-Up (GSU) transformer. It converts the relatively low voltage from the generator (15-25kV) to much higher transmission voltages (138-765kV) to minimize energy loss during long-distance transmission across the power grid.
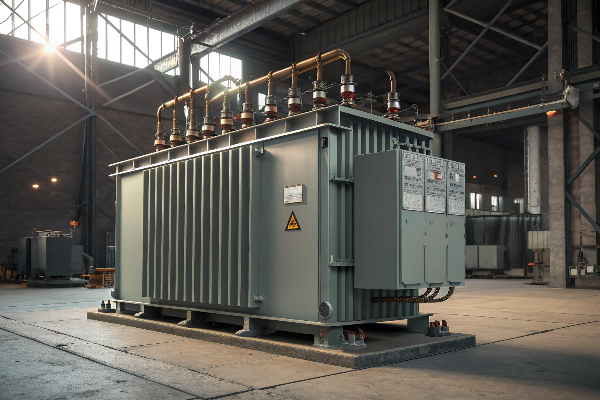

The GSU transformer serves as the critical link between power generation and transmission. I've designed several GSU transformers for renewable energy projects, and their specifications are incredibly demanding. These transformers must be exceptionally reliable since they handle the entire plant output.
Generator Step-Up Transformer Specifications
| Characteristic | Typical Range | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage Ratio | 13.8kV/345kV to 24kV/765kV | Matches generator output to transmission requirements |
| Cooling System | ONAF, OFAF, ODAF | Maintains safe operating temperatures under full load |
| Impedance | 8% to 15% | Controls fault current and system stability |
| Efficiency | >99.5% | Minimizes energy losses |
| Tap Changer | ±5% to ±10% in steps | Adjusts voltage ratio as needed |
Last summer, I was called to a hydroelectric plant in British Columbia where their 30-year-old GSU transformer was showing signs of degradation. We performed oil analysis that revealed dissolved gas compounds indicating insulation breakdown. This early detection allowed us to schedule a replacement before catastrophic failure occurred. The new transformer we designed included advanced monitoring systems that track oil temperature, dissolved gas levels, and winding condition in real-time, allowing predictive maintenance rather than reactive repairs.
Which Type Of Transformer Is Used In Power Applications?
Power applications demand specialized transformers, but choosing the wrong type leads to inefficiency, excessive maintenance costs, or even dangerous failures that can shut down entire operations.
Power applications use three main transformer types: distribution transformers (reducing voltage for end users), power transformers (handling high voltages between generation and distribution), and auto-transformers (efficiently changing voltage levels while sharing a common winding).
 in substation setting Different transformer types in power applications](https://voltoritransformer.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/image-4-different-transformer-types-a-flat-des.png)
The specific transformer used depends on the application's requirements, voltage levels, and operational constraints. In my work designing custom solutions for renewable energy projects, I've found that understanding these distinctions is crucial for system reliability.
Key Transformer Types and Their Applications
| Transformer Type | Voltage Range | Core Design | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Distribution Transformer | Up to 33kV | Core or Shell | Local power distribution, commercial buildings |
| Power Transformer | 33kV to 765kV | Core | Transmission substations, large industrial facilities |
| Auto-transformer | Various | Core | Grid interconnections, voltage regulation |
| Instrument Transformer | Various | Various | Metering, protection systems |
I recently consulted on a solar farm project in Ontario where selecting the right transformer was critical to both performance and budget. The client initially wanted to use standard distribution transformers, but after analyzing their needs, we determined that a specialized solar inverter transformer would provide better harmonics handling and voltage regulation for their particular array configuration. This decision improved overall system efficiency by nearly 3% – a significant gain when dealing with megawatts of power production.
Which Transformer Is Used In A Hydro Power Plant?
Hydroelectric plants face unique challenges with wide load variations, remote locations, and exposure to moisture. Using standard transformers in these environments often results in premature failure and costly downtime.
Hydro power plants typically use three-phase, oil-immersed power transformers with specific design modifications for the unique conditions. These GSU (Generator Step-Up) transformers feature reinforced insulation, specialized cooling systems, and moisture-resistant construction to withstand the hydroelectric environment.
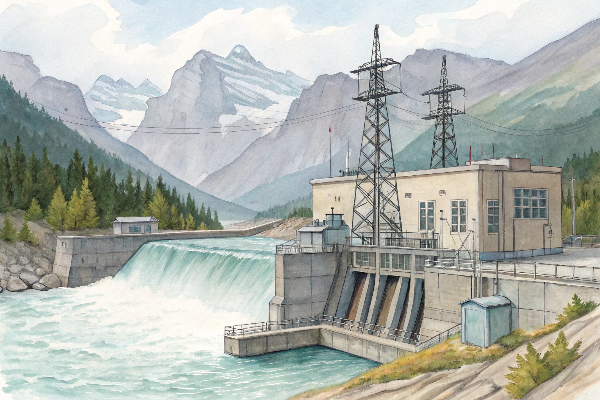

These specialized transformers must be designed to handle the specific operating conditions of hydroelectric facilities. Based on my experience with several hydro projects across Canada, these transformers face unique challenges compared to other power generation types.
Specialized Features of Hydro Power Plant Transformers
| Feature | Purpose | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Enhanced Moisture Protection | Protects against high humidity environments | Extended service life in damp conditions |
| Load-following Design | Handles variable generator output | Maintains efficiency across different water flow rates |
| Ruggedized Construction | Withstands vibration from turbines | Reduces maintenance needs |
| Advanced Monitoring | Detects issues early | Prevents catastrophic failures |
| Biodegradable Oil Options | Minimizes environmental impact | Reduces risk in case of leaks near water sources |
I remember a challenging project for a run-of-river hydro facility in Quebec where space constraints required a compact transformer design without compromising capacity. We developed a custom solution using advanced winding techniques and high-performance core materials that reduced the footprint by 30% while maintaining the required 45MVA capacity. The transformer also included special vibration dampening systems to handle the continuous mechanical stress from nearby turbines.
Conclusion
Transformers are the vital link between power generation and delivery, with different types serving specific roles in power plants. Choosing the right transformer ensures efficiency and reliability in our electrical system.
Need custom power transformers for your renewable energy project? Voltori Energy delivers Canadian-certified solutions engineered for your specific needs.




