The power industry faces mounting environmental pressures while demand grows exponentially. Traditional transformers use mineral oils that pose contamination risks and contribute to carbon footprints, leaving utility companies searching for sustainable alternatives.
Eco-friendly transformer options are available and increasingly popular in the power industry. These include transformers using vegetable-based oils, dry-type transformers requiring no cooling liquids, and smart transformers that optimize energy efficiency while reducing environmental impact through improved materials and manufacturing processes.
](https://voltoritransformer.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/1-first-image-eco-friendly-transformer-options-.png)
The growing focus on sustainability has pushed manufacturers to develop transformers that maintain reliability while reducing environmental impact. Let me walk you through the main eco-friendly transformer alternatives currently available and explain why they matter for your renewable energy projects.
What Is The Alternative To Electric Transformers?
We often hear clients asking if there are alternatives to traditional electric transformers altogether. The existing power infrastructure depends heavily on transformers, but several emerging technologies show promise for specific applications.
Solid-state transformers represent the most viable alternative to conventional electric transformers. These use power electronics to convert voltage levels digitally without large copper windings or cooling oils. They're more compact, efficient, and environmentally friendly while offering enhanced grid control capabilities and reducing raw material requirements.
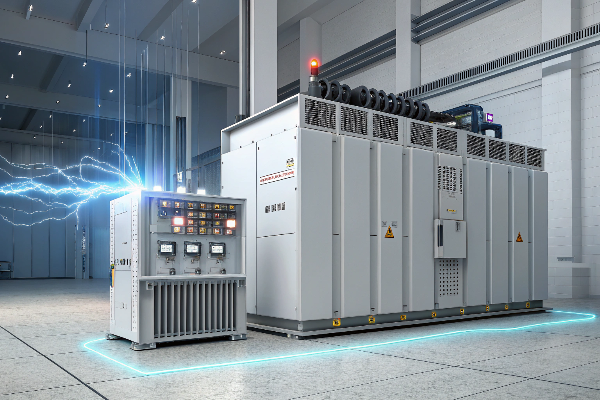

Solid-state transformers utilize semiconductor technology to perform voltage conversion through power electronic converters. Unlike traditional transformers with their bulky copper windings and cooling systems, these devices use silicon carbide or gallium nitride components to convert power at higher frequencies. The benefits extend beyond environmental considerations - they're typically 30-50% smaller and lighter than conventional transformers, making installation easier in space-constrained locations. They also provide superior power quality management and can respond instantly to grid fluctuations. However, they currently face limitations in high-voltage applications and have higher upfront costs than conventional transformers.
Other alternatives include rotary converters for specialized industrial applications and virtual power plants that use software to coordinate distributed energy resources. For smaller off-grid applications, systems can bypass traditional transformers entirely through DC microgrids or direct solar-to-battery configurations. Each alternative has specific use cases but traditional transformers - albeit eco-friendly versions - remain the backbone of our electrical distribution systems for most applications.
What Are The Environmental Impacts Of Transformers?
I've visited countless substations where aging transformers become environmental liabilities. Traditional transformer designs create several significant environmental challenges that many operators don't fully consider until problems arise.
Traditional transformers impact the environment through potential oil leaks and spills, high energy losses generating unnecessary carbon emissions, use of non-renewable resources in manufacturing, noise pollution affecting surrounding communities, and end-of-life disposal challenges with hazardous materials requiring specialized handling.
The comprehensive environmental impact of transformers extends throughout their lifecycle. During manufacturing, transformers require substantial raw materials including copper, steel, and mineral oil derived from petroleum. The extraction and processing of these materials contributes significantly to carbon emissions and habitat destruction. In operation, transformer efficiency directly impacts energy consumption - even a 1% efficiency improvement in large transformers can prevent thousands of tons of CO2 emissions annually.
One of the most immediate environmental risks comes from mineral oil, which typically contains polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in older units. These substances persist in the environment for decades and can cause serious ecological damage when leaks occur. A single transformer can contain hundreds or thousands of liters of this oil. The table below illustrates the comparative environmental impacts of different transformer types:
| Transformer Type | Oil Spill Risk | Carbon Footprint | End-of-Life Recyclability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mineral Oil | High | High | Moderate (oil requires special disposal) |
| Vegetable Oil | High (but biodegradable) | Moderate | Good |
| Dry Type | None | Moderate-High | Excellent |
| SF6 Gas | Low (but extremely high GWP if leaked) | Very High | Poor |
Noise pollution is another often overlooked impact, especially in urban environments where transformers can create constant low-frequency humming that affects quality of life for nearby residents. As renewable energy integration increases, addressing these environmental impacts becomes even more critical for building truly sustainable power systems.
What Is A Green Transformer?
My team at Voltori Energy regularly encounters misconceptions about what constitutes a "green" transformer. The term gets thrown around loosely, but specific technologies and design approaches truly deserve this designation.
A green transformer incorporates environmentally friendly design elements including biodegradable insulating fluids (like vegetable oils), energy-efficient core materials to reduce losses, sustainable manufacturing processes, reduced raw material usage, and smart monitoring systems that optimize performance and extend service life.

Green transformers represent a comprehensive approach to environmental sustainability in power distribution equipment. The core technology often centers around amorphous metal cores, which reduce no-load losses by up to 80% compared to traditional silicon steel. These specialized metal alloys have a non-crystalline, randomly arranged atomic structure that significantly reduces the energy lost during magnetization and demagnetization cycles.
For cooling and insulation, innovative materials play a crucial role. Beyond just using vegetable oils like those from Petro Canada that I mentioned earlier, some manufacturers have developed synthetic esters and natural esters with improved fire safety ratings and biodegradability indices exceeding 95%. These fluids break down naturally within weeks or months rather than decades for mineral oils.
Smart monitoring technologies further enhance the "green" credentials of modern transformers. By continuously monitoring operating conditions, these systems can:
| Monitoring Capability | Environmental Benefit |
|---|---|
| Temperature optimization | Reduced energy losses and extended lifeight |
| Load management | Prevents overloading and unnecessary stress |
| Fault prediction | Avoids catastrophic failures and oil spills |
| Dynamic capacity rating | Maximizes existing infrastructure without replacement |
The manufacturing process itself has also evolved, with some producers implementing closed-loop water systems, solar-powered facilities, and more efficient winding techniques that minimize material waste. A truly green transformer considers its entire lifecycle impact, from raw material sourcing to end-of-life recycling programs that can recover over 90% of components for reuse.
Is Transformer Oil Environmentally Friendly?
I often get asked about transformer oils during project consultations. The answer isn't straightforward - it depends entirely on the type of oil being used and how it's managed throughout the transformer's lifecycle.
Traditional mineral-based transformer oils derived from petroleum present serious environmental concerns including poor biodegradability, toxicity risks, and high carbon footprint from extraction and processing, making them fundamentally unfriendly to the environment despite their excellent technical properties.
The environmental profile of transformer oils varies dramatically across different types. Traditional mineral oils have served as the industry standard for decades due to their excellent dielectric properties and cost-effectiveness, but their environmental credentials are concerning. These petroleum-derived products can persist in soil for decades after spills, potentially contaminating groundwater and ecosystems.
Vegetable-based transformer oils represent the most promising eco-friendly alternative. In Canada, products like those from Petro Canada have gained significant traction in the renewable energy sector. These natural ester fluids are derived from renewable resources like soybean, sunflower, or canola oil. Their biodegradability rate exceeds 95% within 28 days, compared to less than 30% for mineral oils over the same period. While they typically cost about 1.15 times more than mineral oils upfront, as I've observed in our projects, this premium is offset by several advantages:
| Oil Type | Biodegradability | Fire Safety (Flash Point) | Carbon Footprint | Cooling Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mineral Oil | Poor (<30% in 28 days) | Moderate (160-180°C) | High | Good |
| Vegetable Oil | Excellent (>95% in 28 days) | Superior (>300°C) | Low | Good to Excellent |
| Synthetic Ester | Very Good (>80% in 28 days) | Superior (>300°C) | Moderate | Excellent |
Beyond vegetable oils, synthetic esters offer another environmentally improved option, though with a higher carbon footprint from manufacturing. These oils provide excellent technical performance but at a higher cost point that may be justified in environmentally sensitive areas or where fire safety is paramount. The environmental friendliness of any transformer oil also depends significantly on proper handling procedures, containment systems, and end-of-life disposal or recycling practices.
Conclusion
Eco-friendly transformer options are increasingly viable, from vegetable-based oils to solid-state technology that eliminates liquid coolants entirely. These advances allow the power industry to reduce environmental impact without sacrificing performance. For sustainable renewable energy infrastructure, trust Voltori Energy to provide custom-engineered, environmentally responsible transformer solutions across Canada.






